
In line with the philosophies and cultural practices of ancient China, Chinese medicine, with a history of over 2500 years has been embraced by people with their hearts and soul. Whereas Western medicine treats symptoms in isolation, Chinese medicine takes a holistic approach that connects the body-mind-environment. Understanding the historical root of this medication helps us to see why it is still relevant today as well as how its healing practices evolved from ancient documents to contemporary applications.
What were the origins of Chinese medicine?
Chinese medical roots have been traced back more than 2,500 years. These roots are embedded in ancient Chinese philosophy, particularly Taoism. Some individuals like Huang Di (“Yellow Emperor”) contributed to its practice by writing fundamental texts that still have an impact on it today.
The development of Chinese medicine started with such texts as Huangdi Neijing (The Yellow Emperor’s Inner Canon) and Shang Han Lun (Treatise on Cold Injury). They defined diagnosis and treatment by yin-yang theory and five elements. On top of this, new ideas were introduced into Chinese medicine through cultural and medical exchanges along the Silk Road for centuries.
As a result, there was the inclusion of herbs, and, acupuncture among other holistic approaches towards health which expanded into a larger system that still influences many till now; hence making it not only adaptable but also one that seeks balance hence unique among all healthcare traditions.
Who is Huang Di in Chinese medicine history?
Huang Di, also known as the Yellow Emperor, is a legendary figure in Chinese medicine. He is credited with authoring the Huangdi Neijing, one of the foundational texts that outlines the principles of Chinese medical theory.
Huang Di’s contributions to Chinese medicine are pivotal, as the Huangdi Neijing serves as a cornerstone in the understanding of health and disease within the context of Chinese philosophy. This ancient text explores the concepts of Yin and Yang, the Five Elements, and the importance of balancing Qi (energy) to maintain health.
It provides guidelines for acupuncture, herbal medicine, and lifestyle practices that are still followed in Chinese medicine today. Although Huang Di’s historical existence is debated, his influence on the development of Chinese medicine is undeniable.

How did Taoism influence Chinese medicine?
Chinese medicine was largely influenced by Taoism, which emphasized the interconnection between body and nature. The concepts of Qi, Yin, and Yang are fundamental to Chinese Medicine as it is practiced from a Taoist perspective.
Taoism, with its emphasis on balance, flow, and harmony, provided the philosophical foundation for Chinese medicine. The Taoist belief in the interconnectedness of all things is reflected in the holistic approach of Chinese medicine, where health is seen as a state of balance between opposing forces, such as Yin and Yang.
Taoist practices, like meditation and breathing exercises, also influenced the development of therapies like Qi Gong, which focuses on cultivating and regulating energy flow in the body. This alignment with nature and the universe remains central to the practice of Chinese medicine.
What role did the Silk Road play in Chinese medicine's development?
The Silk Road played a crucial role in the development of Chinese medicine by facilitating cultural and medical exchanges. It introduced new herbs, ideas, and techniques from other civilizations, enriching and expanding the practice of Chinese medicine.
As a major trade route, the Silk Road connected China with various civilizations, including those of India, Persia, and the Mediterranean. Alongside goods, medical knowledge and practices were exchanged, leading to the integration of new herbs, treatments, and diagnostic methods into Chinese medicine.
This cross-cultural exchange not only diversified Chinese pharmacopoeia but also introduced concepts such as pulse diagnosis and advanced surgical techniques. The blending of indigenous Chinese knowledge with foreign influences helped shape Chinese medicine into a more comprehensive and sophisticated healing system, enhancing its global relevance.
What are the key texts in Chinese medicine?
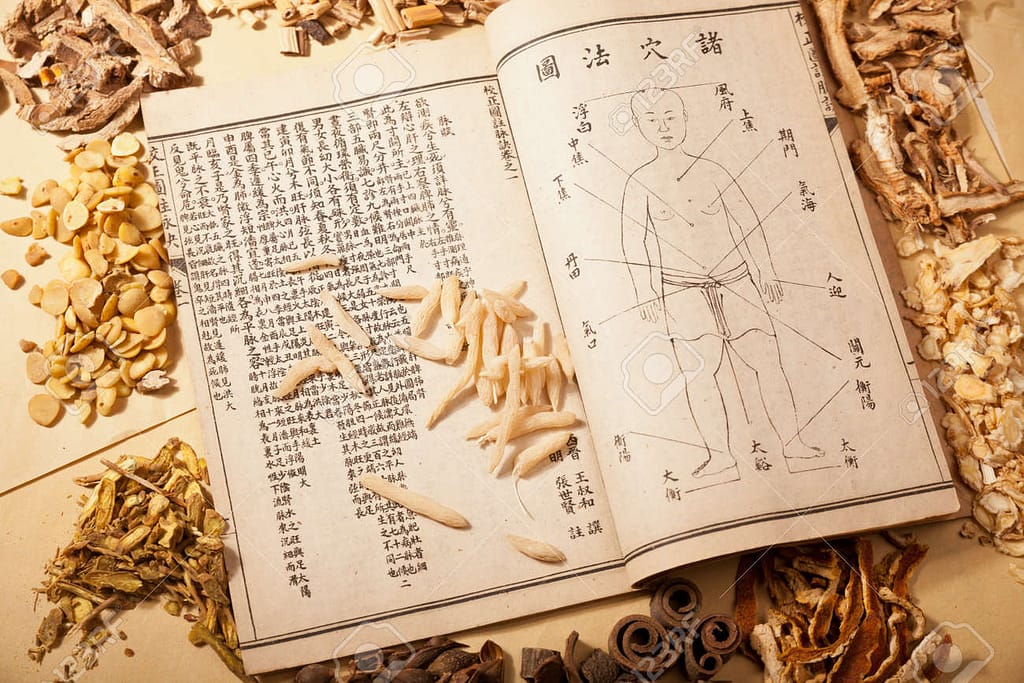
Chinese Medicine’s Key Texts include Huangdi Neijing Suwen, Bencao Gangmu (Compendium of Materia Medica), and Shang-Han Lun (Treatise on Cold Damage). These ancient works serve as the classical texts on medical theory, herbal medicine, and diagnostic techniques that remain influential in Chinese medical practice until today.
The Huangdi Neijing is the most important ancient text of Traditional Chinese Medicine. It outlines principles of health and disease, diagnosis, and treatment. On the other hand, The Treatise on Cold Damage describes diagnosing and treating external pathogens, particularly herbal treatments.
Lastly, the Compendium of Materia Medica is a detailed herbal encyclopedia compiled by Li Shizhen with information about thousands of herbs and their medicinal uses. Other well-known texts like Zhen Jiu Jia Yi Jing or Nan Jing also form an integral part of Chinese medicine over centuries.
How has Chinese medicine evolved over time?
Chinese Medicine has developed from traditional use for centuries up to now which means new cultures have been integrated into it with modern approaches but still maintaining its deep roots around holistic care.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) has undergone considerable adaptation since its inception. Initially centered on herbs as well as acupuncture; it gradually included features from other cultures such as pulse examination from India along with surgical procedures from Persia being some examples.
Now, however, TCM is more comprehensive due to its integration with Western medical practices creating a global healthcare approach that preserves many traditional healing methods under ongoing scrutiny and worldwide researches that confirm their efficacy.
How did Chinese medicine influence other medical systems?
Other medical systems have been influenced by Chinese Medicine, especially in East Asia. These practices include acupuncture and herbal treatments which are now practiced in Japan, Korea, and Vietnam giving rise to very unique healing traditions of their own.
Chinese medicine has reached beyond China, particularly into its neighbors such as Japan, Korea, and Vietnam. In Japan, Kampo is similar to Chinese herbal practices while Qi and Yin-Yang are incorporated in Korean medicine. Dong y or Vietnamese traditional medicine relies heavily on Chinese texts and techniques for reference.
These frameworks adapt and localize Chinese models with indigenous wisdom to form distinct medical traditions. Moreover, the impact of Traditional Chinese Medicine on contemporary Western medicine cannot be ignored especially the Integrative and alternative medicine where there is a growing recognition of acupuncture and herbal therapies.
Wrapping Up!
The history of Chinese healing traditions reveals an ancient practice that has been shaped over time through philosophy, culture as well as cross-cultural interactions. Understanding these fundamentals can help us realize the true scope of holism within TCM itself when considered from its roots to what it stands for today. Even today it ascribes significant insights contained in ancient wisdom that dovetail with scientific knowledge for well-being among diverse populations with different health challenges.

