
Do you think you ever wonder who works behind the curtains to keep modern healthcare running? Well, you may need to ask again because the answer is a functional nurse specialist. They infuse the bridging between the practice of clinical nursing and administrative efficiency, offering comprehensive and effective care.
So, what is a functional nurse specialist and why are they so needed in healthcare? Let’s step into their world of complex responsibilities as well as manage and influence patients and health institutions.
Understanding the Role of a Functional Nurse Specialist(FNS)
A Functional Nurse Specialist (FNS) is an advanced-practice registered nurse with specialized clinical training in specific areas within healthcare settings. They not only deliver direct patient care but also address operational aspects of nursing, thereby improving patient outcomes while streamlining service delivery.
Key Responsibilities:
Clinical Expertise: FNSs have extensive knowledge about their area of specialization which enables them to offer excellent treatment as well as mentor other nurses.
Policy Implementation: They are actively involved in rolling out health policies within units under their jurisdiction so that these practices can be responsive to current health regulations and standards.
Quality Assurance: A significant part of their work revolves around monitoring quality improvement measures for patient care. In this regard, they appraise procedures done accurately to get the desired outcomes thus identifying areas for intervention aimed at bettering such processes.
Fundamental Concepts and Techniques of Functional Nurse Specialist
Sophisticated nurse practices aim to cater fully to the healthcare needs of every patient with the functional approach combining conventional nursing and functional medicine. This position aims at treating diseases to their roots and not merely managing the signs and symptoms. Key concepts and techniques include:
- Holistic Approach: Comprehensive care modification strategies based on lifestyle, nutrition, mental state, environmental factors, and other aspects of health that have been overlooked.
- Advanced Diagnostics: Explaining the use of, in addition to patient examination methods, laboratory examinations of the patient targeted at potential underlying health imbalances.
- Personalized Care Plans: Making each person’s therapy last as long as practical, aimed at the achievement of optimal well-being.
- Education and Empowerment: Assisting patients in reclaiming their health through dieting, lifestyle alteration, and other self-contributory active measures.
By addressing the causes of all illnesses and any precursors of the conditions, Functional Nurse Specialists’ efforts are directed at alleviating assorted medical conditions and enhancing the quality of life.
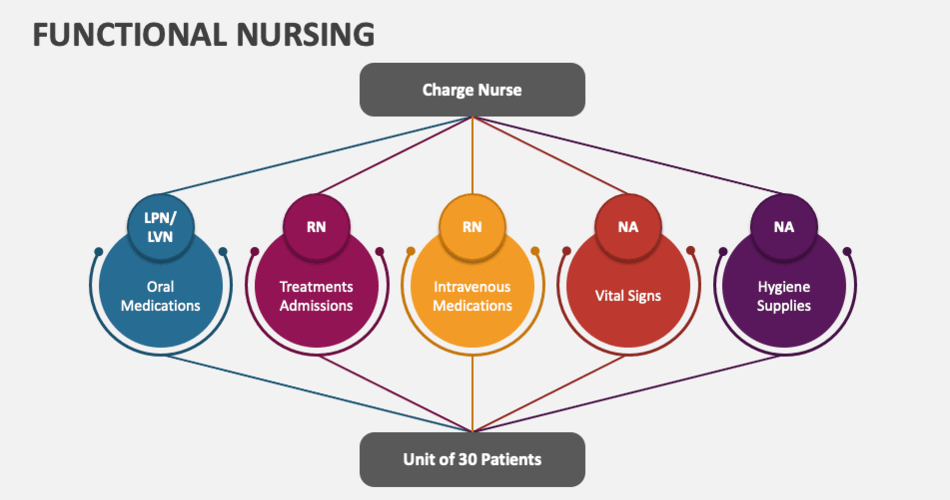
Benefits of Collaborating with a Functional Nurse Specialist
There is a lot to gain by having a functional nurse specialist in your healthcare team. Here are some benefits you should anticipate:
Discovering the Main Cause: Functional medicine does not only focus on symptoms; it aims at finding what triggers particular health problems. This can help one get better results that are also sustainable.
All-Round Approach: In looking into your health, functional medicine takes into account all areas of your life that may affect it. Such an all-inclusive method may lead to more thorough and efficient treatment plans.
Better Life Quality: Functional medicine can greatly enhance people’s lives by addressing foundational issues and designing individual programs for them. You might have raised levels of energy, improved sleep patterns, enhanced moods, or a general state of happiness.
Encouragement: With knowledge provision plus mentorship being part of their work description, these nurses encourage individuals towards self-care responsibility about health matters. Henceforth, people shall have deeper insights into their bodies and be equipped with the necessary skills needed when making decisions regarding personal well-being.
Supplementary Care: Traditional medical care can be supported by functional medicine which could serve as another choice for those who want to be more involved in maintaining good health or have not benefited from usual treatments.
Who Can Benefit from Functional Nurse Specialist? A Guide for Different Needs
The patient population catered for by functional nurse specialist is vast and focuses on individualized care that is based on the cause of the problem. There are particular groups that stand to benefit including:
People with Complex Health Needs: Functional Nurse Specialists assist patients with multi-system health problems through the developmental approach.
Patients Seeking Holistic Care: Appropriate for patients who wish to use both traditional and non1-traditional approaches to healthcare.
Due to their preferences towards a more individual and broad perspective of care, Functional Nurse Specialists are able to manage various health issues across all age ranges.
Specialization and Education
It is an uphill task to become a Functional Nurse Specialist. This must be preceded by a Bachelor of Nursing degree after which they gain clinical experience. Apart from this, they have to take up further specialization with a Master’ degree in a given field of nursing that imparts more skills and knowledge required for this position.
Areas of Specialisation
- Pediatrics
- Gerontology
- Oncology
- Cardiac Care
- Mental Health
Every specialty serves particular groups of patients who need different care hence; making it necessary for FNSs to possess high levels of competence and flexibility.

Ethical Concerns and Advocacy for Patients’ Rights (need supporting page)
Functional nurse specialists also embrace ethical standards and rights to the patients. Their advanced education combined with close contact with clients at different stages equips them with unique skills in handling tough ethical dilemmas that might ensue in clinical practice.
Primary Areas of Ethical Focus
Patient Confidentiality: We have to ensure that all information concerning any given patient is treated as strictly confidential and used in good faith only.
Consent after Providing Adequate Information: It is from them that assurance is supposed to be made that every individual is informed about several treatment options available for his or her condition before blindly choosing any one of them.
Ethics of Decision Making: They mostly often end up heading such committees where tough decisions have to be made once in a while making sure that legal conditions and patients’ welfare are adhered to.
Functional Nurse Specialist with Traditional and Alternative Therapies
Functional Nurse Specialists work together with the providers of traditional and alternative healthcare in an effort to provide a more holistic approach to healthcare issues. The most important aspects of this approach include:
- Collaboration with Traditional Healthcare: Healthcare provision through coordination with physicians and other specialists and treatment-oriented goals.
- Complimentary Methods: Function Nurse Specialists complement treatment with psychotherapies that encompass but are not limited to chiropractic nutrition acupuncture etc.
- Cooperative Therapeutics: Offer the patient with synthetic drugs along with the natural medicine for positive outcomes.
- Preventive and Lifestyle Approach: Suggest a lifestyle alteration, including diet and stress relief for better health retention.
This integrative method results in immediate symptom relief to the patient, however, the more serious and long-lasting factors are also being eliminated.
Empower Yourself: When You Want to Take the Position of Functional Nurse Specialist
Education, training, and certification are some of the steps in becoming a Functional Nurse Specialist. The main steps include:
- Complete Steps Required in Becoming an RN: First begin with a nursing degree and attain a registered nurse license.
- Obtain Functional Medicine Education: Engage in functional medicine by attending relevant institutes and earning their certification such as those provided by IFM.
- Build up Experience: Implement functional medicine practices in reality to advance in a patient-oriented style of care.
- Enhance your skills and experiences: Read up on the latest study and refinements in the field as continuing education.
The steps provided above will position you as an informed, competent, and Functional Nurse Specialist devoted to the comprehensive care of the patient.
Creating a Community: Connecting to Others Out There Practicing as a Functional Nurse Specialist
Communities among the Functional Nurse Specialists can facilitate collaboration and more professionally-related development. The steps to do so are as follows:
Join Professional Organizations: An example includes the American Association of Nurse Practitioners AANP and the Institute for Functional Medicine IFM.
Attend Events Relating to Functional Medicine: Participate in all the relevant functional medicine conferences, workshops, and events online and in person.
Leverage Online Platforms: LinkedIn and similar groups and forums with other professionals.
Seek for a Mentor: Look for seasoned mentors who are willing to advise you on how to proceed and offer their insights.
Strong community bonds boost the knowledge of people within it, improve better care of patients, and prolong the development cycle of Functional Nurse Specialists.
Wrapping Up!
It is impossible to think about the efficiency and progress of the healthcare system without functional nurse specialists. Though they cannot be perceived directly, there is plenty that works out right with the patient’s health, just because it is a functional nurse. Whether it be direct caregiving, mentoring staff members, or implementing strategic policies, all these contributions made by functional nurses toward modernizing medical services cannot be ignored at any point in time.
The next time you walk into the hospital, remember how essential these experts are to ensure that quality treatment is given to you. We must appreciate the multifaceted role of a functional nurse specialist in our healthcare system.

